Super User
LIFE Farm4More – LIFE H2020
LIFE Farm4More - Future Agricultural Management for multiple outputs on climate and rural development
Life Farm4More aims to reduce GHG emissions in the agriculture sector by:
- Creating and characterization of low emissions animal feeds from biorefinery products:
- organic/non-organic grass-legumes press-cakes with/without biochar;
- protein derived ingredients - crude protein (CP); hydrolysed protein; amino acid (AA) and polypeptides (PP) concentrates;
- Testing the new biorefinery sourced feeds in animal trials (cattle, pig and poultry)
- Screening for additional non-feed applications for the generated biorefinery products
- Screening and assessing alternative feed input substrates (ensiled seaweed)
- Assessing economic feasibility
- Establishing and managing a member state/stakeholder group (Ireland, Austria, Denmark) geospecific biorefinery implementation.
- Preparing specific dissemination material for agricultural- and policy level-actors
BMRS role
To optimise seaweed preservation methods by reducing its currently Global Warming Potential (GWP).
Drying seaweeds is the most common preservation method, but it is labour intensive and has a greater Global Warming Potential (GWP) than grass silage. BMRS will replace drying by a novel ensiling process. The new ensiling process will ensure that its nutritional- and monetary-value is maintained, while producing a bi-product, that possesses similar chemical characteristics to that of grass-silage press juice. The seaweed-silage press juice will be fed to the biorefinery as an alternative input substrate whereby its GHG reductions in relation to current seaweed-production techniques will be identified.
Update April 2020
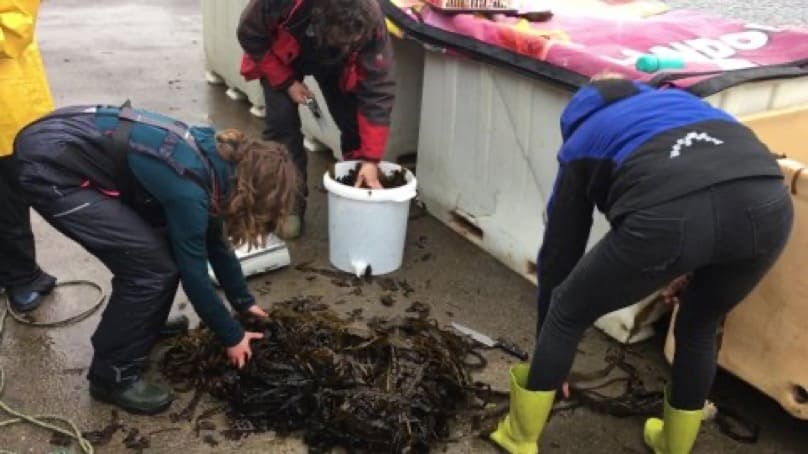 Chopping Alaria for sample buckets and bags for trial 2
Chopping Alaria for sample buckets and bags for trial 2 Vacuum sealed bags before being sealed
Vacuum sealed bags before being sealed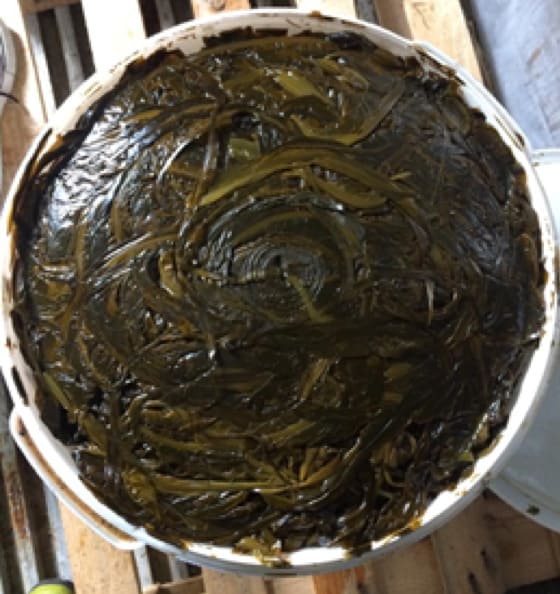 Alaria silage in fermentation bucket 23 days post-harvest from Trial 1
Alaria silage in fermentation bucket 23 days post-harvest from Trial 1
Update September 2023
LIFE Farm4More are attempting to reduce GHG emissions in agriculture by transforming seaweed into protein-rich green biorefinery feedstock.
AgRefine – H2020
The project will involve investigating a novel seaweed-ensiling process as an alternative to drying to preserve seaweeds nutritional and monetary value. The study will also investigate the waste effluent produced by the silage. Seaweed cultivation optimisation strategies will be studied with the aim of maximising seaweed protein and/or mannitol content.
Update September 2020
AgRefine is a Disruptive Innovative Cooperative Entrepreneurial (DICE) education, training and skills development programme rolling out the next generation of Agri Biorefinery and Valorisation Bioeconomy leaders. This project consists of 15 highly interdisciplinary and inter-sectoral PhD projects, each specialising in specific aspects of the bioeconomy.
AgRefine, a European Training Network (ETN), will train 15 Early Stage Researchers (ESRs) in the necessary skills and knowledge to position Europe as the global leader in developing an agri-bioeconomy industry based on the advanced biorefinery technologies.
Aim:
Its overall aim is to address the shortcomings and overcome the weaknesses that current stand-alone AD and biorefinery technologies possess.
BMRS Role:
BMRS will host ESR 7 (Priya Pollard) who will investigate a novel seaweed-ensiling process as an alternative to drying to preserve seaweeds nutritional and monetary value. The study will also investigate the waste effluent produced by the silage. Seaweed cultivation optimisation strategies will be studied with the aim of maximising seaweed protein and/or mannitol content.
BMRS will also provide ESR’s 3 (Eleftheria Papadopoulou), 5 & 8 (Mariana Cerca) with industry experience over their secondments.
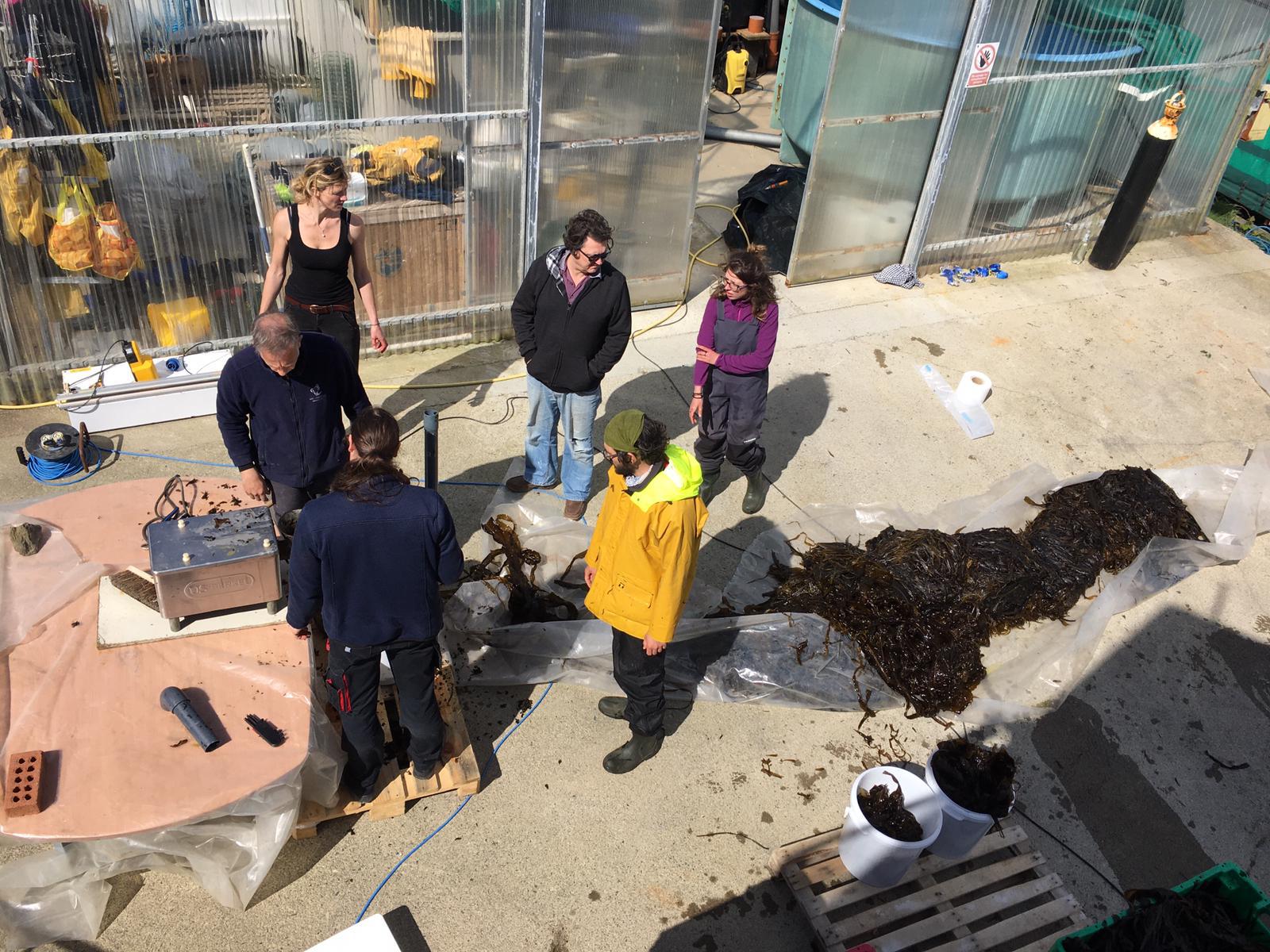 Seaweed being prepped for ensilage
Seaweed being prepped for ensilage Seaweed being compacted into buckets for ensilage.
Seaweed being compacted into buckets for ensilage. Collection tubes labelled and ready for leachate collection
Collection tubes labelled and ready for leachate collection pH of Leachates being monitored on day 21 of ensilage.
pH of Leachates being monitored on day 21 of ensilage. Leachate collected and stored for further analysis.
Leachate collected and stored for further analysis.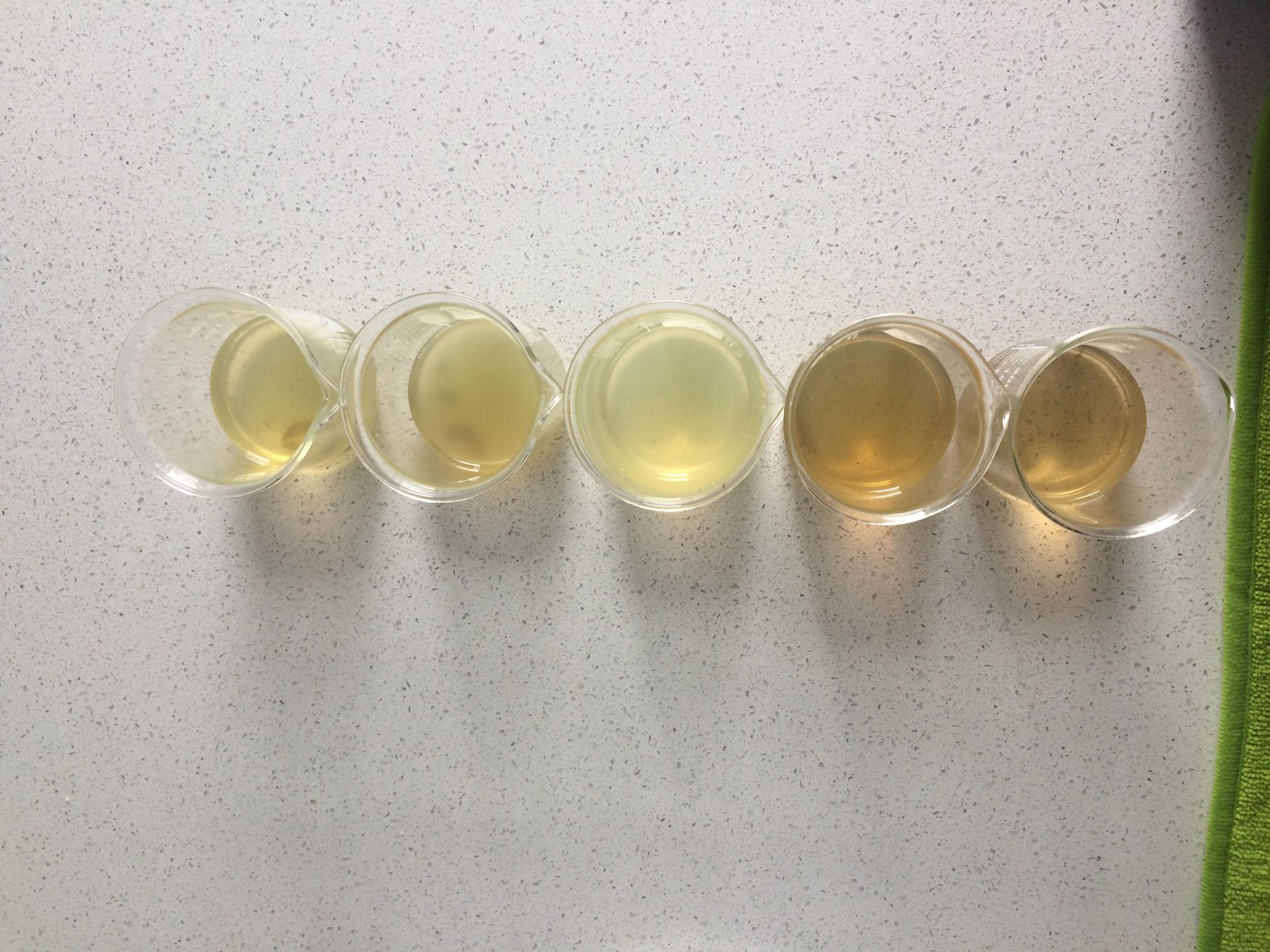 Leachates collected from buckets on day 90 of ensilage.
Leachates collected from buckets on day 90 of ensilage.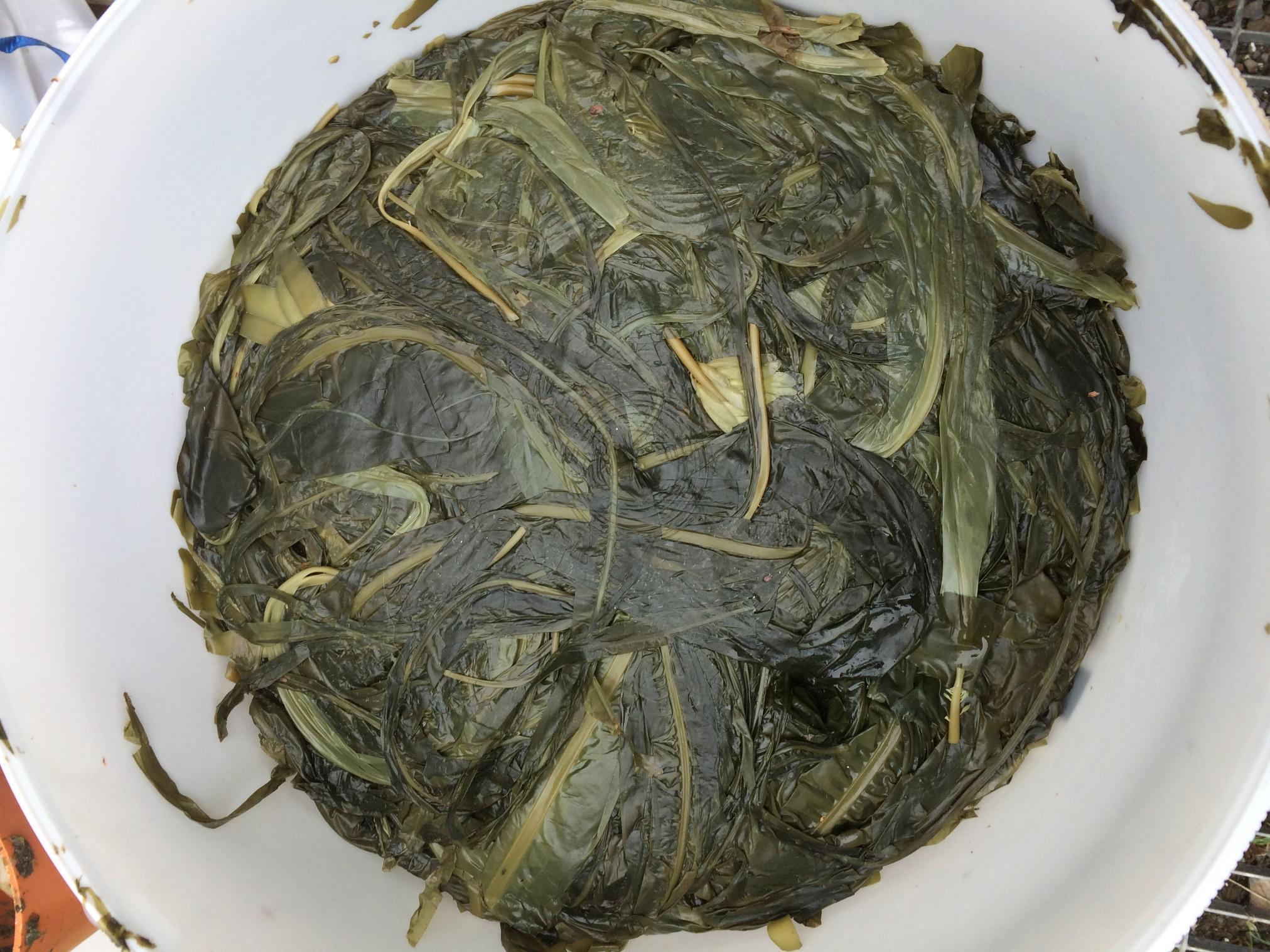 Bucket Day 90 of ensilage.
Bucket Day 90 of ensilage. Bags day 90 of ensilage
Bags day 90 of ensilage Ensiled seaweed and leachate being shipped off to the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) for down-stream processing.
Ensiled seaweed and leachate being shipped off to the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) for down-stream processing. Spraying collectors with Alaria esculenta gametophytes.
Spraying collectors with Alaria esculenta gametophytes.
Small scale silage optimization tests have begun on select kelp species.
 Homogenising kelp with additives before ensilage.
Homogenising kelp with additives before ensilage. Kelp in vacuum sealed bag on day zero of ensilage.
Kelp in vacuum sealed bag on day zero of ensilage.
Vet Services
The tender covers the use of the BMRS facilities to run any land-based tank trials. It also covers the use of the algal hatchery facilities. It requires BMRS to develop and carry out trials using our own initiative.
Impact of ocean acidification on bivalve ontogeny trial
Aim of the research project
The aim of this research project is to assess the impact of climate change related factors such as pH, salinity and temperature on development phenology and growth of bivalve species relevant to Irish culture. Larval rearing will be undertaken in incubators with environmental variables adjusted to the predicted levels (IPCC 2014 Synthesis Report) and controls that replicate optimum conditions. Larval development will be assessed weekly and environmental parameters kept constant and recorded daily.
Update May 2020
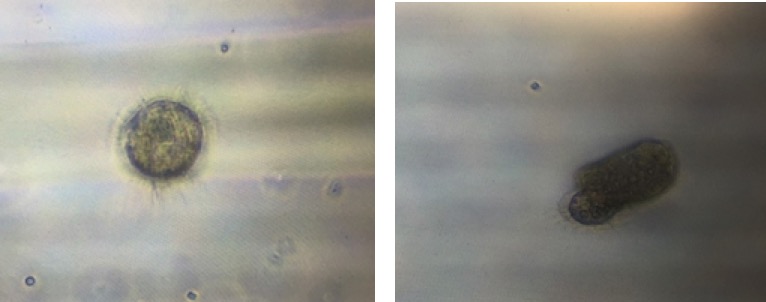 Normal trocophore before treatment inoculation on the left vs distorted trocophore spotted in low pH treatment on the right.
Normal trocophore before treatment inoculation on the left vs distorted trocophore spotted in low pH treatment on the right.
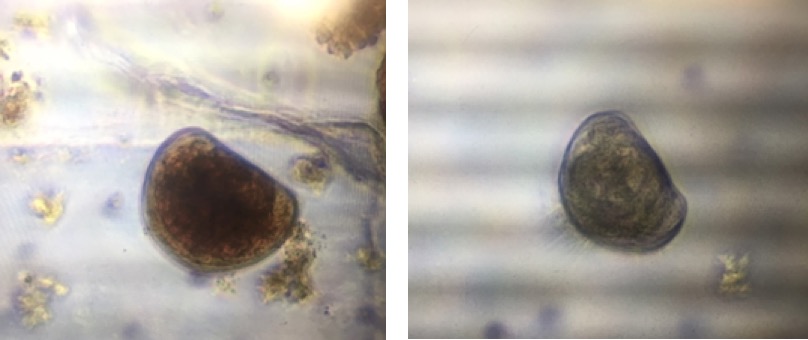 Normal D- larvae in control treatment on the left vs D- larvae with protruding mantle spotted in medium pH treatment on the right both after 5 days in their respective treatments.
Normal D- larvae in control treatment on the left vs D- larvae with protruding mantle spotted in medium pH treatment on the right both after 5 days in their respective treatments.
Update April 2020
 Larvae trap with 30µm mesh sieves
Larvae trap with 30µm mesh sieves Incubators with larval treatments
Incubators with larval treatments
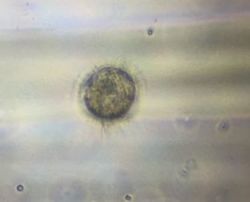 Normal trocophore before treatment inoculation
Normal trocophore before treatment inoculation 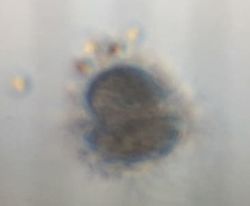 Distorted trocophore spotted in low pH treatment
Distorted trocophore spotted in low pH treatment 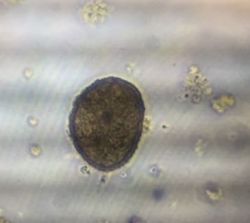 D-larvae sampled in the second week of treatment in high pH and medium salinity treatment
D-larvae sampled in the second week of treatment in high pH and medium salinity treatment
Update March 2020
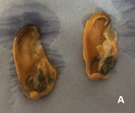
Ripeness assessment and tracking of adult mussels’ developmental stage.
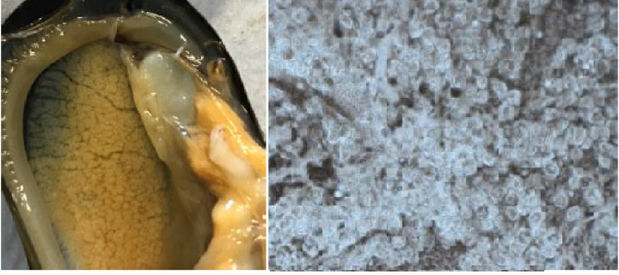 Female mussel in redeveloping phase open on the left and oocytes loosely arranged in follicles on the right.
Female mussel in redeveloping phase open on the left and oocytes loosely arranged in follicles on the right.
 Male mussel in ripe phase open in the left and sperm actively moving on the right.
Male mussel in ripe phase open in the left and sperm actively moving on the right.
Update February 2020
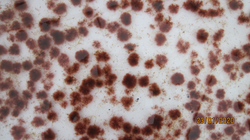
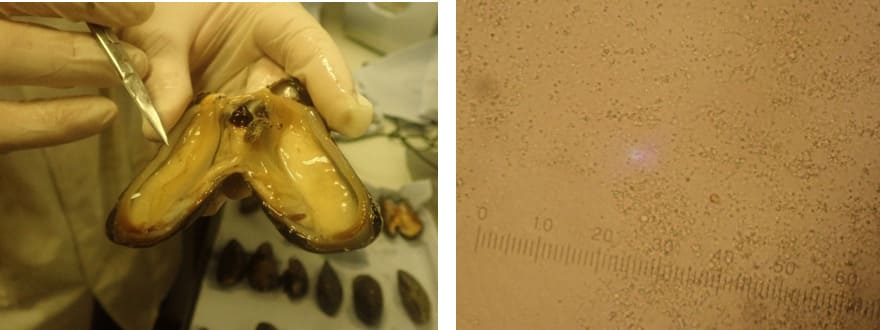 Opened ripe male mussel with mantle obscured by follicles on the left and microscope gonad squash preparation full of active sperm on the right
Opened ripe male mussel with mantle obscured by follicles on the left and microscope gonad squash preparation full of active sperm on the right
 Thermal shock during a spawning trial
Thermal shock during a spawning trial
Update January 2020
Mussel developmental conditioning to assess Mytilus edulis gonad ripeness. Developing/redeveloping individual with the internal organs exposed on the photograph on the left (A) and relatively thick mantle with opaque follicles exposed on the right (B).
Understanding the Evolution of Mitochondrial Genomes in Phaeophyceae Inferred from Mitogenomes of Ishige okamurae (Ishigeales) and Dictyopteris divaricata (Dictyotales)
Liu, Feng, Zhang, Yongyu, Bi, Yuping, Chen, Weizhou, Moejes, Fiona Wanjiku. 2019. Understanding the Evolution of Mitochondrial Genomes in Phaeophyceae Inferred from Mitogenomes of Ishige okamurae (Ishigeales) and Dictyopteris divaricata (Dictyotales). Journal of Molecular Evolution January 2019.
Read the article
Insights on the Sargassum horneri golden tides in the Yellow Sea inferred from morphological and molecular data
Liu, Feng, Liu, Xingfeng, Wang, Yu, Jin, Zhe, Moejes, Fiona Wanjiku, Sun, Song. 2018. Insights on the Sargassum horneri golden tides in the Yellow Sea inferred from morphological and molecular data. Limnol. Oceanogr., 63: 1762-1773.
Read the article.
Organelle genomes of Sargassum confusum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae): mtDNA vs cpDNA
Liu, Feng, Pan,Jun, Zhang,Zhongshan, Moejes, Fiona Wanjiku. 2018. Organelle genomes of Sargassum confusum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae): mtDNA vs cpDNA. Journal of Applied Phycology, March 2018.
Read the article
Environmental Impacts of Experimental Production of Lactic Acid for Bioplastics from Ulva spp.
Helmes, Roel J. K., López-Contreras, Ana M., Benoit Maud Abreu, Helena, Maguire,Julie, Moejes, Fiona and van den Burg, Sander W. K. 2018. Environmental Impacts of Experimental Production of Lactic Acid for Bioplastics from Ulva spp. Sustainability 2018, 10(7), 2462
Read the article
Okin
Vitamin K3, as either menadione nicotinamide bisulfite [MNB] or menadione sodium bisulphite [MSB], is safe for all animal species and authorized for use as a nutritional additive without time limit or maximum content under Council Directive 70/524/EEC. However, both MSB and MNB are sensitive to light and heat and considerable loss can occur in feed manufacture. The inclusion of MNB or MSB in fish diets in a way where their viability and stability is optimized will facilitate greater opportunity for uptake into fish tissue. Studies have shown that MSB may be toxic in mammals and one study found that Atlantic salmon fed MSB (at a concentration of 30 mg/kg) showed reduced performance. In contrast, MNB has been shown to be relatively well tolerated at high concentrations in rainbow trout. As a result of these studies, MNB is the more commonly used form of vitamin K3 added to fish feeds and will be used in this trial.
Thus, OKIN aims to examine the effect of fortifying salmon diets with different levels of vitamin K3 on the concentration of vitamin K in the resulting fillet and identification of the optimized level of inclusion in the diet.
CoCliME
The CoCliME (Co-development of Climate Services for adaptation to changing Marine Ecosystems) project will co-develop and co-produce bespoke, proof-of-concepts or prototype marine ecosystem climate services and a transferable framework for climate services development, to support informed decision making relevant to climate change-related ecological and socio-economic impacts across different coastal regions.
BMRS is involved in WP1 (co-development with users), WP3 (ecological and socio-economic impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems and their users) and WP4 (delivery and dissemination of CoCLiME services and transferable processes). The project is looking at historical data to project the long-term (in 10+ years) effect of climate change on coastal regions using modelling tools. In collaboration with the Marine Institute, we are in charge of the Irish Atlantic case study which focuses on Bantry Bay. Based on initial results, CoCliME is aiming to provide a climate service that will include model projections for the next 20 years on physical environmental conditions and expert opinion on how these changes might affect harmful phytoplankton and microbes.
BMRS has created questionnaires and surveys, and conducted interviews for engaging with different stakeholders involved in aquaculture in Bantry Bay (producers and processors), and have completed Engagement Points 1 and 2.
Methane Project
The project aims to investigate, extract and test anti-methanogenic compounds from Irish seaweeds on rumen fluid. The project will screen native Irish seaweeds and identify suitable candidates that demonstrating any anti-methanogenic properties. This will be followed by the investigation of potential cultivation techniques of the seaweed species of interest. The project will also look at initial stabilisation and conservation techniques so that the biomass maintains it anti-methanogenic potency. Finally, the project will address the applicability of the resulting seaweed product as a potential feed additive, particularly for ruminants including cattle. The product will be subjected to thorough assessments including, but not limited to, environmental impact, health and safety and techno-economic assessments.
To date, researchers at BMRS have developed a sampling protocol that must be adhered to for all seaweed sampling. A seaweed identification flipbook was also created to help researchers identify the seaweed in the field. Below is the current draft of the protocol that has been tested on four separate occasions. Amendments may be made during this early stage in order to ensure that a useful and well-thought out protocol is applied for the remainder of the project. Four sites in West Cork for collecting samples have been identified. Samples are being analysed for bromoform, total bromine and moisture content by Reading Scientific Services Ltd (RSSL) whom we were put in contact with by Dr Abraham Venter. Samples are kept in the -80C freezer awaiting freeze-drying once RSSL is ready to receive the samples.
Advise and comments from Pete Donlon (BIM), Noel Lee (Connemara Seaweed Company), and Prof. Juliet Brodie (Natural History Museum London; co-author of the “Seaweeds of Britain and Ireland” book)
Update May 2020
Newspaper Articles
Independent.ie
Red seaweed used in animal feed 'could cut methane emissions from cattle here by 60pc'
Afloat.ie
Red Seaweed Cultivation for Animal Feed Could Help Meet Government Climate Targets
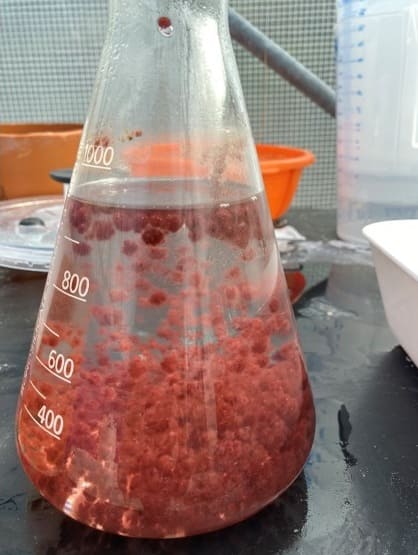
 The researcher Dee McElligott checking Asparagopsis armata tetrasporohytes under the microscope.
The researcher Dee McElligott checking Asparagopsis armata tetrasporohytes under the microscope.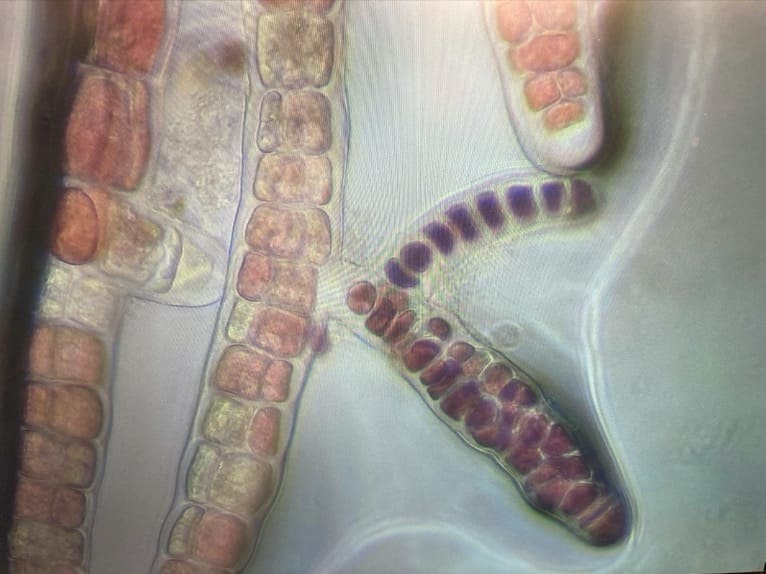 New growth from Asparagopsis armata tetrasporohyte from the cultures
New growth from Asparagopsis armata tetrasporohyte from the cultures
Update April 2020
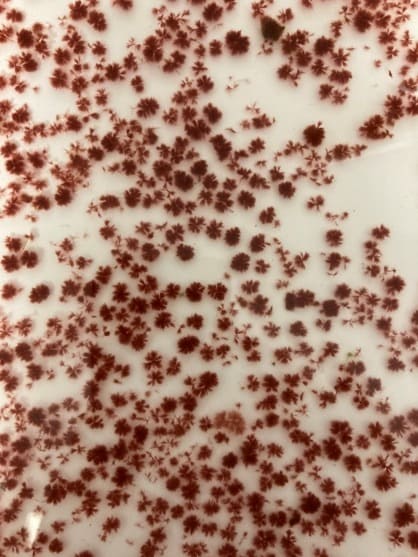
New growth pom poms from our Asparagopsis armata cultures
Update January 2020
As part of the MERCS research project, we are working hard to try innovative ways of growing new species of seaweed, some of them with considerable success.
Pictures: Asparagopsis armata tetrasporophytes cultures: